Last updated on December 28th, 2023
Chvostek sign
Chvostek sign is a facial clinical sign usually performed to assess hypocalcemia – abnormally low serum calcium levels. The Trousseau sign is another clinical sign that is suggestive of hypocalcemia.
Chvostek sign can be defined as a visible spasm of the ipsilateral perioral muscles in response to mechanical stimulation of the facial nerve. It is commonly seen in postoperative tetany.
This phenomenon was first observed by Franz Chvostek (1835-1884). He was an Austrian surgeon. Later Nathan Weiss, a physician also from Austria, reported the same clinical findings.
How to pronunce Chvostek sign?
Chvostek sign pronounced as vaa-stuhk sine
What are the other names for Chvostek sign?
- Chvostek-Weiss sign
- Schultze’s sign
- Schultze-Chvostek sign
- Face sign
How to assess the Chvostek sign?
You can assess the Chvostek sign by tapping with fingertips on the cheekbone in front of the tragus.
Negative Chvostek sign
If there was no facial contraction in response to the stimulation of the facial nerve indicates a Negative Chvostek sign.
However, according to a study, 29% of participants who had hypocalcemia had a Negative Chvostek sign.
Therefore, you can’t rule out hypocalcemia even if the patient had a negative Chvostek sign. Always remember to correlate serum calcium levels.
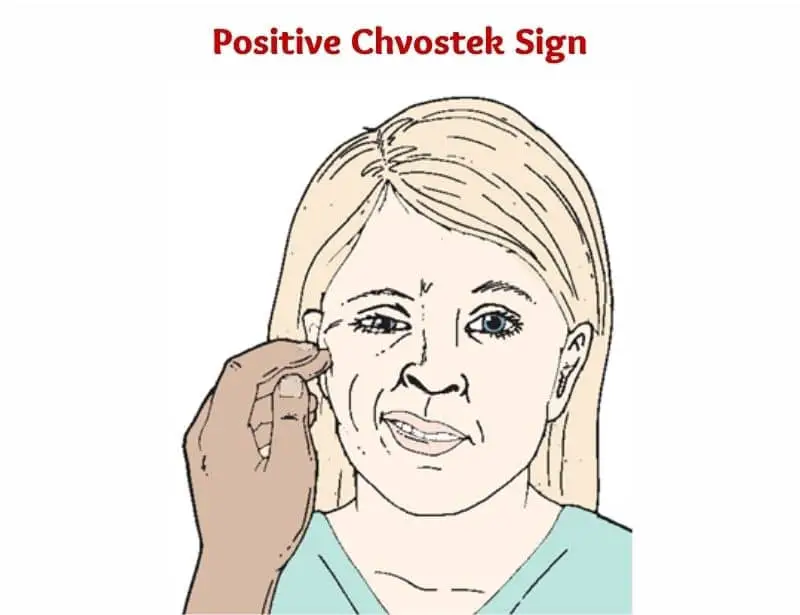
Positive Chvostek sign
If the physical examination of the facial nerve produces twitching near the mouth and nasal area, it indicates a positive Chvostek sign.
When interpreting the positive Chvostek sign, you should be careful. Because evidence suggests that normal individuals also had positive Chvostek sign.
In addition, a study also showed that increased serum calcium levels (hypercalcemia) are significantly associated with positive Chvostek sign. Which is the opposite of what is commonly stated in medical reference.
What are the causes of positive Chvostek sign?
Possible causes for positive Chvostek sign include:
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Respiratory alkalosis
- Kidney failure
- Hyperventilation
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Hypomagnesemia
Treatment of positive Chvostek sign
The treatment for the positive Chvostek sign is correcting the underlying disorder.
For example, correcting hypocalcemia with calcium gluconate.
Conclusion
Chvostek sign is traditionally performed to assess hypocalcemia.
However, evidence shows the Chvostek sign is not highly specific or sensitive to determine hypocalcemia independently. Another clinical sign for which is more strongly associated with hypocalcemia is
However, evidence shows the Chvostek sign is not highly specific or sensitive to determine hypocalcemia independently.
Therefore, you should always correlate with the patient’s lab results along with the findings of the physical examination.
Review Trousseau’s sign, which is a significant indicator of hypocalcemia.
Reference
White, F. (2009). Physical signs in medicine and surgery. Museum Press.



Comments are closed.