In this article, we will explore Alfaro-LeFevre’s 4-Circle Critical Thinking (CT) model.
Related Articles:
What Are Critical Thinking Indicators (CTIs) In Nursing?
15 Attitudes of Critical Thinking in Nursing (Explained W/ Examples)
What is Critical Thinking in Nursing? (Explained W/ Examples)
How to Improve Critical Thinking Skills in Nursing? (24 Strategies W/ Examples)
What is the 4-Circle CT Model?
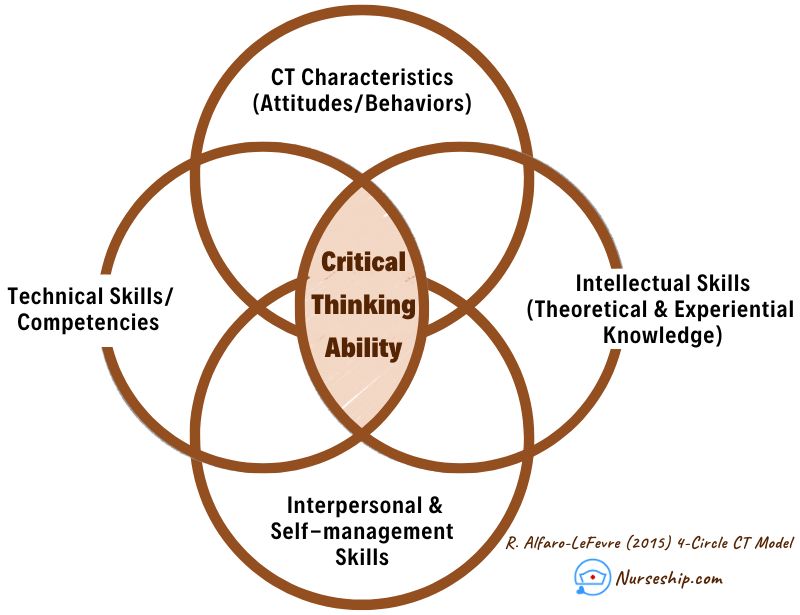
The 4-Circle Critical Thinking Model is a framework designed to help individuals develop and enhance their critical thinking skills.
It was created by Rosalinda Alfaro-LeFevre, a nurse and educator who has written extensively about critical thinking in healthcare and nursing practice.
The 4-Circle Critical Thinking Model consists of four interconnected circles, each representing a different aspect of critical thinking.
Elements of the 4-Circle CT Model
The 4-Circle Critical Thinking (CT) model breaks down critical thinking into four distinct components, each serving as a building block for the overall process.
1. Personal Characteristics
The first component, referred to as personal characteristics, involves a set of intellectual behaviors such as attitudes, beliefs, and values.
These personal traits play a crucial role in activating one’s thinking abilities.
2. Intellectual Skills
The second component, intellectual and cognitive abilities encompasses the knowledge, skills, and comprehension related to nursing processes and decision-making. This aspect involves understanding the actions and steps necessary for effective nursing practice.
3. Interpersonal and Self-management Skills
The third component is interpersonal and self-management skills. These abilities are centered around facilitating therapeutic communication and gathering relevant patient information.
This includes skills related to interacting with patients, their families, and fellow healthcare professionals.
4. Technical Skills
The fourth and final component, technical abilities, involves the specialized knowledge and expertise in nursing procedures.
This component covers the practical aspects of nursing, including the specific techniques and methods that are part of the nursing discipline.
These CTIs are descriptions of behaviors that foster critical thinking within the context of clinical practice.
The mastery of critical thinking is achieved through the harmonious integration of attributes across these four dimensions.
See Also:
- Nursing Concept Map (FREE Template)
- Clinical Reasoning In Nursing (Explained W/ Example)
- 8 Stages Of The Clinical Reasoning Cycle
- What is the “5 Whys” Technique?
- What Are Socratic Questions?
Conclusion
In summary, Alfaro-LeFevre’s 4-Circle Critical Thinking (CT) model breaks down critical thinking into four interconnected components: personal characteristics, intellectual and cognitive abilities, interpersonal abilities and self-management, and technical abilities.
Each component contributes uniquely to the development of critical thinking in clinical contexts, and a series of critical thinking indicators is proposed as benchmarks for assessing competence in each dimension.
Recommended Readings
Critical Thinking Indicators (CTIs)
Critical Thinking, Clinical Reasoning, and Clinical Judgment: A Practical Approach
Applying Nursing Process: The Foundation for Clinical Reasoning