OLD CARTS and OPQRST are two mnemonic frameworks commonly used in medical and nursing assessments to systematically gather information about a patient’s symptoms, particularly in the context of history-taking and evaluation of conditions.
Both OLD CARTS and OPQRST are valuable assessment tools that serve different purposes and cater to different areas of clinical evaluation, with OLD CARTS being more comprehensive and applicable to a wider range of symptoms, while OPQRST is particularly useful for pain assessment and pain-related conditions.
In this post, we will discuss the differences between OLD CARTS and OPQRST.
Related: OLD CARTS Acronym (Explained W/ Questions)
OLD CARTS
OLD CARTS Acronym Stands for:
- Onset
- Location
- Duration
- Character
- Aggravating factors
- Relieving factors
- Timing
- Severity
Purpose of OLD CARTS:
OLD CARTS provide a comprehensive approach for assessing a wide variety of symptoms, not limited to pain. It aims to gather a holistic understanding of the patient’s symptom experience.
Usage of OLD CARTS:
This framework can be applied across different medical specialties to evaluate diverse symptoms, helping healthcare professionals form a complete picture of the patient’s condition.
Scope of OLD CARTS:
OLD CARTS cover a broad spectrum of symptom assessment beyond pain, taking into consideration various dimensions like the nature of the symptom, its impact, and potential triggers.
OPQRST
OPQRST Acronym Stands for:
- Onset
- Provocation/Palliation
- Quality
- Region/Radiation
- Severity
- Timing
Purpose of OPQRST:
OPQRST is primarily used for assessing pain and discomfort. It focuses specifically on understanding pain characteristics, factors that worsen or alleviate the pain, and the temporal aspects of the pain.
Usage of OPQRST:
OPQRST is commonly employed in situations where pain assessment is crucial, such as emergency medicine or situations where a patient’s pain is a key concern.
Scope of OPQRST:
While OPQRST is tailored for pain evaluation, it might not cover the comprehensive range of symptoms that OLD CARTS addresses.
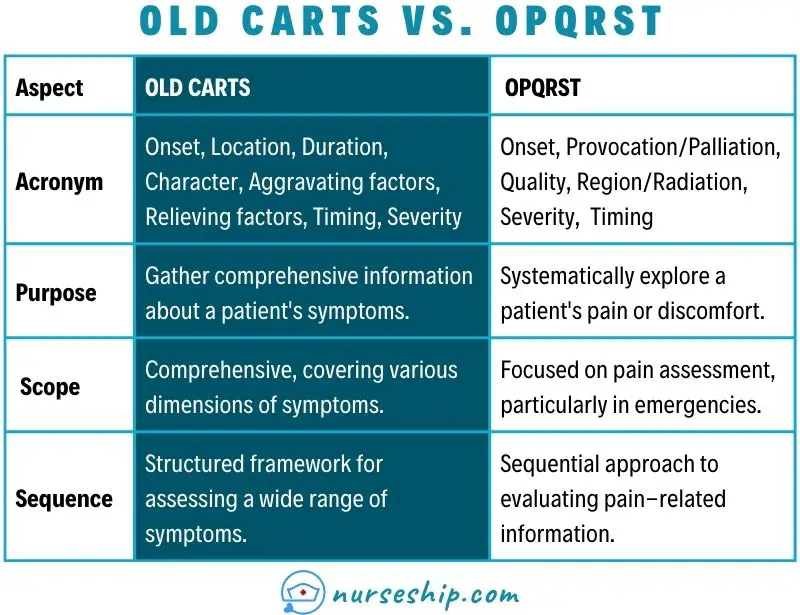
OLD CARTS vs. OPQRST
| Aspect | OLD CARTS | OPQRST |
| Acronym | Onset, Location, Duration, Character, Aggravating factors, Relieving factors, Timing, Severity | Onset, Provocation/Palliation, Quality, Region/Radiation, Severity, Timing |
| Purpose | Gather comprehensive information about a patient’s symptoms. | Systematically explore a patient’s pain or discomfort. |
| Scope | Comprehensive, covering various dimensions of symptoms. | Focused on pain assessment, particularly in emergencies. |
| Sequence | Structured framework for assessing a wide range of symptoms. | Sequential approach to evaluating pain-related information. |
| Holistic View | Provides insights into the overall symptom experience. | Focuses primarily on pain characteristics and factors. |
| Applicability | Suitable for a broader range of symptoms and assessments. | Particularly useful for pain assessment and pain-related conditions. |
| Components | Includes additional aspects like location, aggravating and relieving factors. | Doesn’t incorporate factors like location and aggravating/relieving aspects. |
| Medical Usage | Widely applicable across various medical assessments. | Often utilized in emergency medicine and pain evaluation. |
| Information Gain | Provides a comprehensive picture of the patient’s condition. | Offers in-depth details about the nature of pain. |
See Also:
- 10 Components Of Nursing Health History
- What Is Nursing Assessment?
- Nursing Concept Map (FREE Template)
Conclusion
To sum up, both OLD CARTS and OPQRST are valuable tools for healthcare professionals and nurses to gather essential information about a patient’s symptoms.
OLD CARTS offer a broader approach, suitable for a wide array of symptoms, while OPQRST is specialized for pain assessment.
Depending on the clinical context and the nature of the patient’s complaints, healthcare providers can choose the framework that best suits their assessment needs.