In this article, we will explain what is the Nursing Process, and the 5 steps of ADPIE.
The nursing process, also known as ADPIE, encompasses five key stages:
1. Assessment,
2. Diagnosis,
3. Planning,
4. Implementation, and
5. Evaluation.
These stages serve as the foundation for providing comprehensive and individualized care to patients.
Throughout this article, we will explore each component of the nursing process, highlighting the importance of assessment in gathering subjective and objective data, the differentiation between nursing and medical diagnoses, the significance of developing SMART goals and outcomes in the planning stage, the implementation of evidence-based interventions, and the crucial role evaluation plays in assessing the effectiveness of the care provided.
You may also want to check out What is Critical Thinking in Nursing?
What is Nursing Process?
The nursing process refers to a systematic and organized approach that nurses use to provide patient-centered care.
It involves a series of interconnected steps designed to assess, diagnose, plan, implement, and evaluate the care provided to individuals or groups.
The nursing process serves as a framework for delivering effective and holistic healthcare, ensuring that patients’ physical, emotional, and psychosocial needs are addressed comprehensively.
Definition of the Nursing Process
The nursing process can be defined as a methodical series of problem-solving steps employed to identify and manage the health problems presented by patients.
What are the 5 Stages of the Nursing Process?
The five steps of the nursing process, nicknamed as ‘ADPIE’ represents the core elements of the nursing process.
The acronym ADPIE stands for Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation.
Every stage plays a vital role in delivering patient-centered care and serves as a structured framework for nurses to provide efficient healthcare.
Here’s a breakdown of each component:
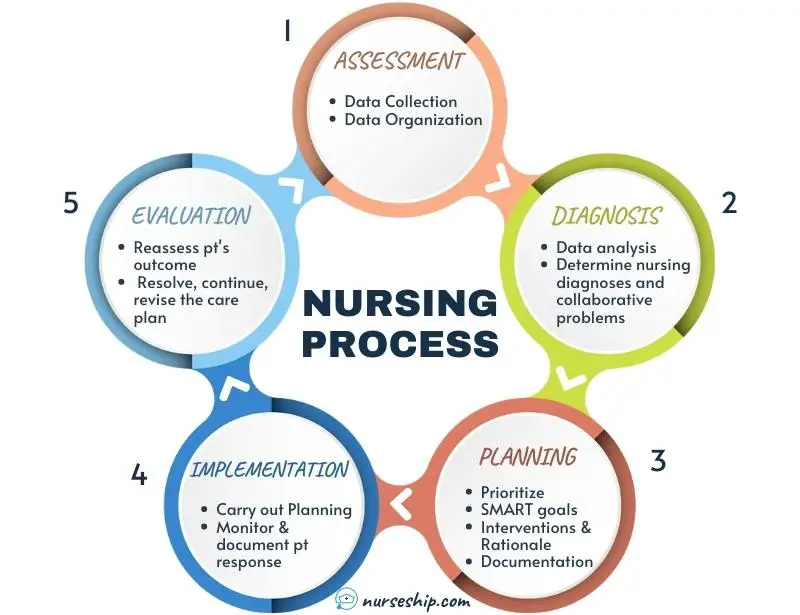
1. Assessment
Learn More About Nursing Assessment.
Assessment is the initial stage of the nursing process, where nurses gather vital information about the patient’s health status.
Its primary purpose is to establish a baseline and identify any actual or potential health problems. There are various types of assessments, including comprehensive, focused, and ongoing assessments.
To ensure effective assessment, nurses rely on various sources of data such as patient interviews, physical examinations, medical records, and laboratory tests.
Tips for conducting a thorough assessment include active listening, observing the patient holistically, and documenting findings accurately and promptly.
2. Diagnosis
In the nursing process, diagnosis refers to the identification of health problems based on the assessment data collected.
It is important to differentiate between nursing diagnosis and medical diagnosis. Nursing diagnoses are unique to the nursing profession and focus on the patient’s response to illness or potential health problems.
There are different types of nursing diagnoses, including actual, risk, and wellness diagnoses. Nurses use guiding factors such as signs, symptoms, and patient priorities to select the most appropriate diagnoses.
Nursing diagnostic statements comprise two components: i. the problem or health alteration and ii. its underlying cause or contributing factors.
3. Planning
Planning is a crucial step in the nursing process, as it involves prioritizing and setting goals and outcomes that guide the implementation of care.
Goals are broad statements that describe the desired results, while outcomes are specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
Well-formed goals exhibit characteristics such as being client-centered, evidence-based, and culturally appropriate.
Nurses collaborate with patients and interdisciplinary healthcare teams to develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses the identified nursing diagnoses and incorporates evidence-based interventions.
4. Implementation
Implementation is the stage where nurses put the care plan into action.
It involves executing the planned interventions and providing direct patient care. Nurses utilize their clinical skills, knowledge, and expertise to deliver interventions that are aligned with the established goals and outcomes.
Additionally, they provide education, support, and emotional guidance to promote patient well-being and facilitate their recovery process.
The relevance and rationale of interventions should always be communicated to patients, ensuring that they actively participate in their care and understand the intended outcomes.
5. Evaluation
Evaluation is the final step of the nursing process, assessing the effectiveness of the care provided and the achievement of the predetermined goals and outcomes.
Nurses collect data, compare the patient’s response to the expected outcomes, and analyze any variances that may have occurred.
If goals are met, the care plan may be concluded. However, if goals are not fully achieved, nurses modify the care plan accordingly, ensuring that it meets the evolving needs of the patient.
Evaluation is paramount in improving the quality of patient care and helps find ways to improve the healthcare system.
See Also
- Nursing Concept Map (FREE Template)
- 15 Attitudes of Critical Thinking in Nursing (Explained W/ Examples)
- Clinical Reasoning In Nursing (Explained W/ Example)
- How To Improve Critical Thinking Skills In Nursing? 24 Strategies With Examples
- What is the “5 Whys” Technique?
- What Are Socratic Questions?
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 5 stages of the nursing process (acronym for ADPIE) serve as a framework for delivering quality nursing care that is holistic, patient-centered, and evidence-based.
Through a systematic approach of assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation, nurses are able to provide individualized care that meets the unique needs of each patient.
The nursing process is essential for enhancing patient outcomes, improving healthcare delivery, and promoting the overall well-being of individuals and communities.
It is a cornerstone of nursing practice that empowers nurses to make informed decisions and deliver care that makes a difference in people’s lives.
Recommended Readings
Potter, P.A., Perry, A.G., Stockert, P. and Hall, A. (2013) Fundamentals of Nursing
Kozier & Erb’s Fundamentals of Nursing: Concepts, Process and Practice, 11th edition




